- Recommended name
- Tetrodotoxin
- Synonyms
- Tetrodontoxin, Maculotoxin, Babylonia japonica toxin 1, Fugu poison, Tarichatoxin, Spheroidine
- Recommended acronym
- TTX
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
- Name
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Note
- No conclusive production. TTX detected in cultures isolated from bivalve molluscs (England)
- Name
- Vibrio cholerae
- Note
- No conclusive production. TTX detected in cultures isolated from bivalve molluscs (England)
- Name
- Prorocentrum cordatum
- Note
- Potential links to P. minimum but not proven or subsequently confirmed in other studies
- Name
- Pseudomonas
- Note
- TTX detected in Pseudomonas sp isolated from TTX -positive organisms e.g. pufferfish
- Name
- Pseudoalteromonas
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
- Name
- Actinobacteria
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
- Name
- Bacillus
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
- Name
- Roseobacter
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
- Name
- Alteromonas
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
- Name
- Aeromonas
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
- Name
- Nocardiopsis
- Note
- Linked to potential production from Genus
Vector Species
- Name
- Tutufa
- Note
- T. Noguchi, J. Maruyama, H. Narita, K. Hashimoto Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in the gastropod mollusk Tutufa lissostoma (frog shell) Toxicon, 22 (1984), pp. 219-226
- Name
- Pugilina
- Note
- H. Narita Tetrodotoxin, with special reference to its origin and the mechanism of toxification Seikatsu Eisei, 35 (1991), pp. 2-15
- Name
- Hapalochlaena maculosa
- Note
- Posterior salivary gland D.D. Sheumack, M.E.H. Howden, I. Spence Occurrence of a tetrodotoxin-like compound in the eggs of the venomous blue-ringed octopus (Hapalochlaena maculosa) Toxicon, 2 (1984), pp. 811-812
- Name
- Pseudopotamilla occelata
- Note
- T. Yasumoto, M. Yotsu, A. Endo, M. Murata, C.Y. Kao Interspecies distribution and biogenetic origin of tetrodotoxin and its derivatives Pure Appl. Chem., 61 (1989), pp. 505-508
- Name
- Atergatis floridus
- Note
- T. Noguchi, A. Uzu, K. Koyama, K. Hashimoto Occurrence of tetrodotoxin as the major toxin in xanthid crab Atergatis floridus Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish, 49 (1983), pp. 1887-1892
- Name
- Zosimus aeneus
- Note
- D. Yasumura, Y. Oshima, T. Yasumoto, A.C. Alcala, L.C. Alcala Tetrodotoxin and paralytic shellfish toxins in Philippine crabs Agric. Biol. Chem., 50 (1986), pp. 593-598
- Name
- Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda
- Note
- A. Kungsuwan, Y. Nagashima, T. Noguchi, Y. Shida, S. Suvapeepan, P. Suwansakornkul, K. Hashimoto Tetrodotoxin in the horseshoe crab Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda inhabiting Thailand Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 53 (1987), pp. 261-266
- Name
- Parasagitta
- Note
- E.V. Thuesen, K. Kogure, K. Hashimoto, T. Nemoto Poison arrowworms: a tetrodotoxin venom in the marine phylum Chaetonnatha J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 116 (1988), pp. 249-256
- Name
- Pleurobranchaea maculata
- Note
- Very high concentrations quantified from New Zealand Sea Slugs
- Name
- Lagocephalus sceleratus
- Note
- Pufferfish
- Name
- Flaccisagitta
- Note
- E.V. Thuesen, K. Kogure, K. Hashimoto, T. Nemoto Poison arrowworms: a tetrodotoxin venom in the marine phylum Chaetonnatha J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 116 (1988), pp. 249-256
- Name
- Astropecten
- Note
- J. Maruyama, T. Noguchi, J.K. Jeon, T. Harada, K. Hashimoto Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in the starfish Astropecten latespinosus Experientia, 40 (1984), pp. 1395-1396
- Name
- Yongeichthys criniger
- Note
- T. Noguchi, Y. Hashimoto Isolation of tetrodotoxin from a goby Gobius criniger Toxicon, 11 (1973), pp. 305-307
- Name
- Atelopus
- Note
- Y.H. Kim, G.B. Brown, H.S. Mosher Tetrodotoxin: occurrence in atelopid frogs of Costa Rica Science, 189 (1975), pp. 151-152
- Name
- Steromphala umbilicalis
- Note
- Silva, M., Azevedo, J., Rodriguez, P., Alfonso, A., Botana, L.M. & Vasconcelos, V. 2012. New gastropod vectors and tetrodotoxin potential expansion in temperate waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Marine Drugs 10(4): 712–726. Portugal - LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Phorcus lineatus
- Note
- Silva, M., Azevedo, J., Rodriguez, P., Alfonso, A., Botana, L.M. & Vasconcelos, V. 2012. New gastropod vectors and tetrodotoxin potential expansion in temperate waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Marine Drugs 10(4): 712–726. Portugal - LC-MS/MS
- Name
- Charonia
- Note
- Europe - first TTX poisoning case Confirmed in patient's blood LC-MS and MBA
- Name
- Mytilus edulis
- Note
- Mussels from around N. Europe including England LC-MS/MS confirmation
- Name
- Mytilus edulis
- Note
- Mussels from around N. Europe including England, Netherlands LC-MS/MS confirmation
- Name
- Planocera
- Note
- Miyazawa et al. (1986) Whole body flatworms
- Name
- Lineus fuscoviridis
- Note
- Whole body ribbonworms Miyazawa et al. (1986)
- Name
- Tubulanus punctatus
- Note
- Whole body ribbonworms Miyazawa et al. (1986)
- Name
- Cephalothrix linearis
- Note
- Whole body ribbonworms Ali et a 1990 high toxicity, of up to 22,000 MU/g proboscis and 13,600 MU/g body, in terms of TTX
- Name
- Babylonia japonica
- Note
- T. Noguchi, J. Maruyama, Y. Ueda, K. Hashimoto, T. Harada Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in the Japanese ivory shell Babylonia japonica Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish., 47 (1981), pp. 901-913 Toxin isolated and crystalised + MBA
References
- Noguchi et al, 2011
- Pufferfish Gastropods
- Noguchi, T, Arakawa, O, 2008
- Flatworms: Planocera spp. Ribbonworms: Lineus fuscoviridis, Tubulanus punctatus, Cephalothrix linearis Gastropoda: Charonia sauliae, Charonia lampas lampas, Babylonia japonica, Tutufa lissostoma, Zeuxis siquijorensis, Niotha clathrata, Niotha lineata, Cymatium echo, Pugilina ternotoma, Pleurobranchaea maculata Polychaeta: Pseudopolamilla occelata Xanthidae crabs: Atergatis floridus, Zosimus aeneus Horseshoe crab: Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda Arrowworms: Parasagitta spp., Flaccisagitta spp. Starfish: Astropecten spp. Pisces, Goby, Amphibia: Yongeichthys criniger, Tarica spp., Notophthalmus spp. Newts: Cynopsis spp., Triturus spp. Frogs: Atelopus spp., Colostethus sp., Polypedates sp., Brachycephalus spp.
- Sonoyama et al, 2020
- Pufferfish Canthigaster valentini
- Tsai et al, 2006
- Xanthid crabs: Demania cultripes, Demania toxica, Demania reynaudi, Lophozozymus incisus, Lophozozymus pictor and Atergatopsis germaini
- Noguchi et al, 2006
- Pufferfish: Takifugu snyderi
- Rodriguez et al, 2008
- Charonia lampas lampas - Spain
- McNabb PS et al, 2014
- Paphies australis Pleurobranchaea maculata New Zealand
- Gerssen et al, 2018
- Mussels and oysters Netherlands
- Cole et al, 2015
- Dried pufferfish
- Vlamis et al, 2015
- Greek shellfish plus potential links to Prorocentrum minimum
- Bentur et al, 2008
- Lagocephalus sceleratus in the eastern Mediterranean
- Leao et al, 2018
- Bivalve molluscs from NW Spain
- Yotsu et al, 1987
- Pufferfish and Pseudomonas sp.
- Turner, A.D et al, 2017
- TTX accumulation was detected in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas), native oysters (Ostrea edulis) common mussels (Mytilus edulis) and hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria), but not found in cockles (Cerastoderma edule), razors (Ensis species) or scallops (Pecten maximus).
- Turner, A.D et al, 2015
- Mussels and oysters - England (Mytilus Edulis and Crassostrea gigas) Vibrio parahaemolyticus and one strain of V. cholerae isolated from TTX-positive Pacific oysters
- Jal and Khora, 2015
- Bacterial production possible vectors
- Magarlamov et al, 2017
- TTX-producing bacteria (detection, distribution and migration in aquatic systems)
- Katikou and Vlamis, 2017
- Prevalence of TTXs in European vectors Pufferfish Bivalves Gastropods
- Fernandez-Ortega et al, 2008
- First TTX intoxication case in Europe - Trumpet Shellfish Charonia sauliae
- Turner, A.D. et al, 2018
- Marine nemertean Cephalothrix simula Pseudomonas luteola isolated from C. simula Vibrio alginolyticus from the nemertean Tubulanus annulatus
- Dhanji-Rapkova et al, 2021
- Pacific Oysters (Crassostrea gigas)
- Magarlamov et al, 2017
- Vibrio, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Alteromonas, Streptomyces, Roseobacter
- Biessy et al, 2020
- Paphies australis
- Vlasenko, A.E., 2020
- Cephalothrix simula
- Suo et al, 2022
- Planocera multitentaculata
- Bedry et al, 2021
- Lagocephalus sceleratus Torquigener flavimaculosus
- Katikou, P, 2017
- Torquigener flavimaculosus
- Lage et al, 2023
- The Edible Crabs Afruca tangeri and Carcinus maenas
- Structure
-
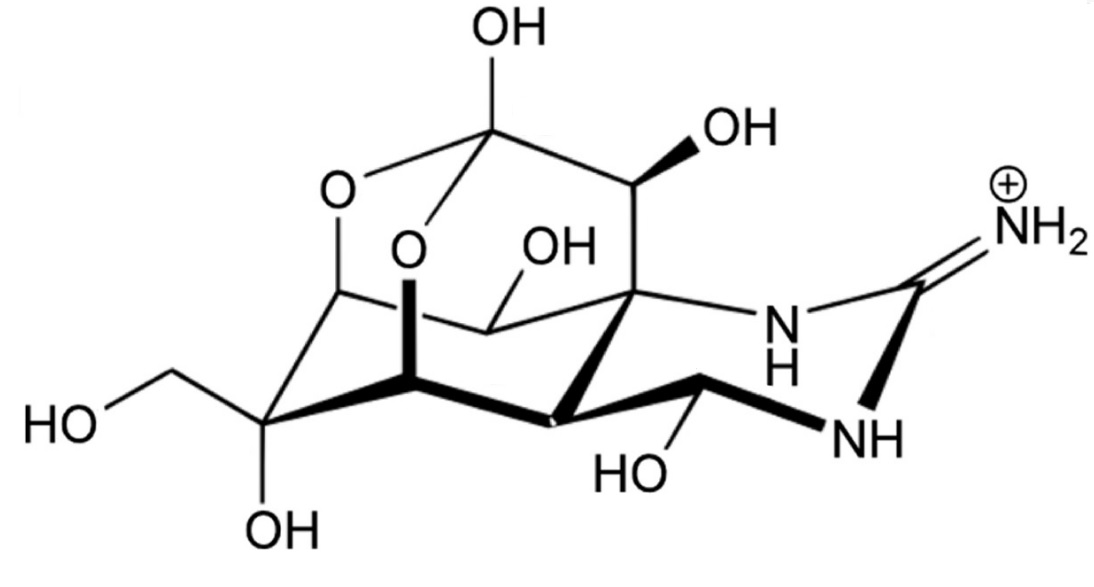
- Formula
- C11H17N3O8
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 319.101563
- Molfile
- n/a
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- C([C@@]1([C@H]2[C@@H]3[C@H](N=C(N[C@@]34[C@@H]([C@@H]1O[C@]([C@H]4O)(O2)O)O)N)O)O)O
- Alternative SMILES
- C(C1(C2C3C(N=C(NC34C(C1OC(C4O)(O2)O)O)N)O)O)O
- InChi key
- CFMYXEVWODSLAX-QOZOJKKESA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- 1S/C11H17N3O8/c12-8-13-6(17)2-4-9(19,1-15)5-3(16)10(2,14-8)7(18)11(20,21-4)22-5/h2-7,15-20H,1H2,(H3,12,13,14)/t2-,3-,4-,5+,6-,7+,9+,10-,11+/m1/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- True
- Chem files
References
- Moczydlowski E.G, 2013
- Chemical structure, chemistry, molecular biology, action mechanisms
- Bane et al, 2014
- Chemistry, toxicity, source, distribution and detection
- Certified
- True
- Certified links
-
- National Research Council Canada
NRC CRM-TTX is a certified instrument calibration solution for use in the analytical determination of tetrodotoxin (TTX). Each ampoule contains approximately 0.5 mL of a solution of TTX dissolved in filtered, aqueous 1 mM acetic acid. - Merck (Sigma Aldrich)
>98% powder - product T8024 - not certified - Enzo
Product BML-NA120-0001 >98% powder - not certified - CIFGA
Product CRM-03-TTXs Certified solution containing TTX, plus additional analogues 4,9-anhydro TTX and 4-epi TTX Purity >97% Solution 1mM acetic acid; 0.5 mL supplied - Thermo Scientific Chemicals
1mg material - product code 13187663 (Fisher Scientific) Thermo Scientific Acros product = 328560010 99% purity - not certified - Nacalai tesque
1mg TTX in citric acid buffer Product 32775-51(purity ≥94%, Kyoto, Japan) - not certified - Wako
Wako pure chemical industries (purity >99%, Osaka, Japan) - not certified - Affixscientific Corporation
Affixscientific Corporation (purity ≥98%, Fremont, CA, USA) - not certified - Tocris Bioscience
Tocris Bioscience (purity ≥98.8%, Bristol, UK), Cat number = 1078 Sold as TTX citrate - not certified - Biorbyt Ltd
Biorbyt Ltd. (Cambridge, UK) Sell 4,9-anhydroTTX (Cat No: orb1693171) CAS 13072-89-4 Purity 98% SMILES: O[C@H]1[C@]23[C@@]4([C@@]5([C@](CO)(O)[C@]1(O[C@](O)([C@]2(O[C@@]4(N=C(N)N3)[H])[H])O5)[H])[H])[H] Formula: C11H15N3O7 - not certified - Latoxan
Latoxan (Valence, France) - not certified
- National Research Council Canada
- Non certified reference material
- True
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- True
- Validated
- True
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- True
- Validated
- True
- Official
- Puffer toxin. Environmental Health Bureau, ministry of Health and Welfare. The Manual for Methods of Food Sanitation Tests II, vol 2, Environmental Health Bureau, Food Hygiene Association, Tokyo, Japan (1978) pp21-22
References
- Moczydlowski E.G, 2013
- Structure recognition
- Wang et al, 2015
- Functional assay using cardiomyocyte-based impedance biosensor
- Turner et al, 2017
- HILIC-MS/MS validation (single lab)
- Turner et al, 2023
- Interlaboratory evaluation of multiple LC-MS/MS methods and a commercial ELISA for TTX in mussels and oysters
- Bane et al, 2014
- Detection method review plus chemistry, source and distribution
- Kogure et al, 1988
- Tissue culture assay
- Hamasaki et al, 1996
- Tissue culture assay
- Katikou and Vlamis, 2017
- Advances in analysis methods
- EFSA, 2017
- Includes detection methods at time of risk assessment opinion
- Rodriguez et al, 2012
- LC-MS/MS - applied to pufferfish
- Silva et al, 2012
- LC-MS/MS applied to gastropods
- EURL, 2017
- https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/CRLMB/web/public_documents/seccion/crlmb_standard_operating_procedures.htm
- Regulatory status
- False
References
- EFSA, 2017
- Risks for public health related to the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and TTX analogues in marine bivalves and gastropods
- Staatscourant 38280 - Dutch legislation, 2017
- https://zoek.officielebekendmakingen.nl/stcrt-2017-38280.pdf Legislation for TTX in the Netherlands, 29th June 2017 - NVWA/2017/5265 A limit value of 44 μg/kg in live bivalve molluscs from Dutch production areas shall be set for the presence of TTX in live bivalve molluscs. Above this value, the NVWA will take measures as referred to in Annex II, Chapter II, under C and D of Regulation (EC) No 854/2004 and Article 6 of the Commodities Act Regulation on live bivalve molluscs
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- Paralytical Shellfish Poisoning
- Organ system toxicity
- Neurotoxicity
- Risk assessment
- True
- Molecular targets known
- True
- Molecular targets
- Voltage dependent sodium channel (site 1)
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- True
- TEF available
- True
Risk assessment References
- EFSA, 2017
- Risks for public health related to the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and TTX analogues in marine bivalves and gastropods
TEF References
- EFSA, 2017
- WHO, 2016
- Based on the i.p. toxicity to mice, relative toxicities of TTX analogues 10 μg/kg b.w. for TTX (Noguchi, Onuki and Arakawa, 2011), 70 μg/kg b.w. for 11-deoxy-TTX (Bane et al., 2014), 420 μg/kg b.w. for 6,11-dideoxy TTX (Jang and Yotsu-Yamashita, 2007), 16 μg/kg b.w. for 11-oxo-TTX (Nakamura and Yasumoto, 1985; Yotsu-Yamashita et al., 2003), 64 μg/kg b.w. for 4-epi-TTX (Nakamura and Yasumoto, 1985; Munday, 2014), 60 μg/kg b.w. for 6-epi-TTX (Yasumoto et al., 1988b), 490 μg/kg b.w. for 4,9-Anhydro-TTX (Nakamura and Yasumoto, 1985), 54 μg/kg b.w. for 11-nor-TTX–6(S)-ol (Yotsu et al., 2014) 70 μg/kg b.w. for 11-nor-TTX–6(R)-ol (Endo et al., 1988). WHO expert group concludes currently that: • Need to establish TEFs for TTX analogues commonly found in bivalves. • Need for comparative studies on the oral toxicity of TTX congeners. World Health Organization & Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2016). Toxicity equivalence factors for marine biotoxins associated with bivalve molluscs. World Health Organization. https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/250663
- Notes
- Andrew Turner
- Contact